Computer Forensics Glossary
Note: The terms in this glossary may have other uses in other fields. The uses discussed here are for general use in computer science, and more specifically, in computer forensics.
Acquisition: The stage in a computer forensics investigation wherein the data involved is collected. Often the means used is a bit-by-bit copy or a forensic working images of the hard disk or other media in question.
Active Files: Data on a computer that is not deleted and is generally accessible and readily visible to the user under normal use.
Allocated space / sector / block: The logical area on a hard disk or other media assigned to a file by the Operating System (See Unallocated)
Allocation Block: (see block, cluster): A contiguous group of sectors, which is the smallest amount of space, assigned to a file by an operating system such as Microsoft Windows.
Application: Commonly known as a Program, or (sometimes) Software. The software used to access and create files or documents. Microsoft Word and Corel WordPerfect are applications that work with word processing documents. Microsoft Excel and Lotus 1-2-3 are applications that work with or spreadsheets.
ASCII: Stands for “American Standard Code for Information Exchange.” Pronounced “Ass-key.” Often referred to as “ASCII text.” ASCII assigns a numerical code for each character on a keyboard; hence ASCII text is often comprehensible to humans without much interpretation.
Attribute: See File Attribute.
Audit Trail: A chronological record of system activities on a computer or network security system that may keep track of user actions such as logins, file access, and other activities.
Back door: A means of accessing or controlling a computer that bypasses normal authentication, while remaining hidden from the casual user. A backdoor may be a program that has been installed surreptitiously, or may be a hidden function of a legitimate program.
Backdoor Trojan: A generic name for Trojan horse programs that open a backdoor and allow an unauthorized user remote access to a computer.
Backup: A copy of data that is kept as an emergency measure against data loss in a system or media failure, and/or for the purpose of keeping archival data. Backups may be compressed or encrypted, and are usually kept separate from the system containing the active version of the data that is being backed up.
Backup Server: A computer on a network that is designed to be used to back up data from other computers on the network. A Backup Server may also be used as a File Server, a Mail Server or as an Application Server.
Backup media: The media on which backup data is kept. May be almost any form of media, such as tapes, CD-ROM, DVD, external hard disks, floppy diskettes, magneto-optical disks, WORM disks, Zip disks, Jaz disks, and many others.
Bit: The smallest unit of data, consisting of a zero or a one, stands for “binary digit.”
Bitstream or bit-by-bit copy: A copy of every consecutive sector on a hard disk or other media, without regard to allocation of data. Sometimes confused with mirroring.
Block: An allocation block, as referred to in the Macintosh Operating System.
Browser: See web browser.
Buffer: An area of memory used to temporarily hold data. May be written to a buffer file.
Buffer file: A file written from data in a buffer.
Burn: The process of creating a CD-ROM or DVD.
Byte: Eight consecutive bits. The unit in which computer storage and computer memory is measured. The amount of data necessary to make a single character (such as a letter or a number) of data. Part of the words kilobyte (KB), megabyte (MB), gigabyte (GB), terabyte, petabyte.
Cache: French for “hide.” A storage area where frequently accessed data may be kept for rapid access. There are three main types of cache: disk cache, memory cache, and program cache. See these entries for further explanation
CD-ROM: Stands for Compact Disk – Read Only Memory. A plastic disk able to hold approximately 650MB to 700MB of data. A common storage medium for data.
Chain of Custody: As in other fields, a record of the chronological history of (electronic) evidence.
Cluster: Also known as allocation blocks, a cluster is a contiguous group of sectors that is the smallest amount of space assigned to a file by an operating system such as Microsoft Windows. Clusters generally range in size from 4 sectors to 64 sectors.
Compressed file, zipped file: A file that has been encoded using less space than the original file in its uncompressed state. A zipped file may contain more than on compressed file.
Computer Forensics: A practice and methodology that may involve any or all of the following: electronic imaging, electronic discovery, forensic analysis of discovered information, preparation of information in a manner useful to the client or court, presentation of findings to the client or attorney, such as in written, oral and/or electronic reports, testimony in a court of law, when necessary, by an expert witness, including deposition and jury trial.
Cookie: In Internet or browser usage, a small file accessed by a web browser and written to the user’s computer. A shortened form of the term, “magic cookie,” cookies are used for tracking, authenticating, and maintaining information about users, generally to ease interaction between a website and a user. Cookies stored on a user’s computer often contain the times and dates that the user accessed a given website.
Corrupt Data, Corrupt File: A file that is damaged. Damage may have occurred inadvertently during transmission, copying, through operating system error, physical damage to the media on which the data was stored, or though other means.
Darkweb: A part of the Deep Web that is used for anonymous and semi-anonymous communication and websites and which generally requires TOR or the equivalent for access.
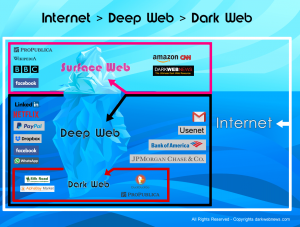
Deep Web: A part of the Internet (about 95% of it) that is not indexed by Google, Bing, or the like and is generally not accessible by web browsers such as Internet Explorer, Edge, and Chrome. Includes databases, internal networks, communities and resources.
Default: A setting or value automatically assigned without user intervention.
Deduplication (“De-duping”): A process performed on a collection of data from multiple sources, whether from several files, several different locations or computers, or from within a collective email file. The process is designed to yield one unique copy of ant given record, file, or email.
Delete: To cause a file or email to move from an active or live state to an ambient state, usually performed by moving a file to the trash or recycle bin on a computer, or by selecting a file and then pressing the delete [Del] key. Deleted files, while generally not removed from the computer until overwritten, are nonetheless invisible to the user.
Desktop (1): In a Graphical User Interface (GUI), such as Windows or the Macintosh OS, the view of files and folders visible before a user opens any windows. The desktop is actually a graphic view of an invisible folder stored on the computer’s hard disk.
Desktop (2): A desktop computer.
Desktop computer: A stand-alone computer that is generally designed to be connected to a keyboard and monitor (although some desktop computers, such as the Macintosh iMac, have the monitor integrated), as distinct from a laptop, and from a Server.
Directory: A hierarchically arranged listing of files stored on a hard disk or other media. The topmost directory is the root directory. Subsequent directories nested within the root directory are called subdirectories. In a GUI, a directory appears as a file folder.
Disk: Generally a hard disk. Floppy diskettes are often referred to as disks.
Disk cache: RAM used to speed up access to stored data. May be part of a computer’s RAM, or may be RAM integrated into the disk drive itself.
Disk Mirroring: Data copied to another hard disk or to another area on the same hard disk in order to have a complete, identical copy of the original.
Dot: A period that is used as part of a filename, or as part of a Web address. It is pronounced “dot.” For instance, a file named “glossary.doc” would be spoken as “glossary dot doc.” Similarly, a web address, such as www.yahoo.com would be spoken as “W-W-W dot yahoo dot com.”
Download: The transfer of data between two computers, generally over a network. One may download a file from the Internet, for instance. Commonly used as a misnomer for “copy.” For instance, a common mistake is to say that one downloaded a file from a diskette, when a file is copied (not downloaded) from a diskette.
E-mail: Electronic mail. Messages transmitted over a computer network or networks, directed to a given user, either individually or in bulk. Email may be stored in a largely text format, or in an encrypted form. Microsoft Outlook stores email messages in an encrypted file; most other email programs store messages primarily as text.
Encryption: A process to render a file unreadable to unauthorized persons or devices.
Exabyte: 1024 Petabytes
Extension, File Extension: Part of a file’s name, usually follows a “dot,” or period in a file name. Some operating systems, such a Microsoft Windows, depend on the extension to know what program is used to open the given file. Microsoft word documents, for instance have “.doc” as their extension.
Filename: The name of a file. Sometimes refers to the name of a file minus its extension.
File Attribute: Properties associated with a file that are kept with the file directory listing. Such attributes include the date and time the file was last accessed, created, or modified,
File Server: A computer on a network that is used to store files from and for multiple users on the network. A file server may also be used as an Application Server, a Backup Server, or as a Mail Server. May be used as a backup for the computers on the network.
File signature: Information contained within a file that identifies its type, even though the file’s extension may have been altered.
File slack: Information at the end of a cluster that has not been completely filled, or overwritten by a file. The file may end before the end of the cluster, hence the cluster may contain data from a previous file
Floppy diskette, floppy: A square-shaped enclosure holding a rotating flexible plastic magnetically coated disk used for data storage. At this writing, the 8″ and 5.25″ variety of floppy diskette is obsolete, and the 3.5″ variety is approaching obsolescence. The most common floppy diskettes hold 1.44 MB of data.
Folder: in a GUI, a folder is the representation of a directory and may contain files and other, nested folders.
Forensic copy: See Forensic Image.
Forensic image: A forensically sound and complete copy of a hard drive or other digital media, generally intended for use as evidence. Such copies include unallocated space, slack space, and boot record. A forensic image is often accompanied by a calculated Hash signature to validate that the image is an exact duplicate of the original.
GIF: A common format for storage of digital images. An acronym for Graphic Interchange Format. Pronounced “Jiff.” GIFs have the file extension “gif”
Gigabyte (GB): 1024 megabytes (MB), or 1,048,576 KB, or 1,073,741,824 bytes. Often considered (incorrectly) to be one billion bytes.
GUI: Graphical User Interface. An image and icon-based interface designed to make manipulation of computer data easy. Common GUIs are Microsoft Windows and the Macintosh OS.
Hard disk: Currently the primary storage medium for data on most computers, Consists of a sealed chassis containing a rapidly spinning metal-coated platter, or stack of platters that are magnetically encoded as data is written to them by enclosed magnetic read/write heads.
Hash, hash value: A hash is a number generated from a string of text. A hash value may be generated for a single file, or for an entire hard disk. A matching hash virtually guarantees that a copy is identical to the original. It does not absolutely guarantee this.
HTML: An authoring language, written in text that is used to create documents for access on the World Wide Web. Such documents may be web pages, or otherwise enhanced documents or email messages. Stands fro Hypertext Markup Language.
Instant Messaging: Abbreviated as IM. A text-based electronic communication in real time. It is similar to a telephone call in its immediacy; it is different in that it is generally text-based.
IP Address (IPv4): An electronic identifier for a specific computer or device on the World Wide Web or other (internal or external) electronic network using the TCP/IP protocol. An IP address is a series of four numbers separated by periods (“dots”), Each number is a value from 0 to 255. An example could be 192.168.55.207 “IP” stands for “Internet Protocol.”
IP Address (IPv6): Like IPv4, An electronic identifier for a specific computer or device on the World Wide Web or other (internal or external) electronic network using the TCP/IP protocol. An IPv6 address is a series of eight groups of four hexadecimal digits with each groups being separated by colons, for example 2002:0ac7:234e:ad42:0000:7b2e:0371:7224, but is sometimes abbreviated.
ISP: Internet Service Provider. A provider of access to or connection to the Internet. Some large ISPs include Earthlink, Yahoo, Roadrunner, SBC Global.
JPEG: A common format for storage of digital images. An acronym for Joint Photographic Experts Group. Pronounced “jay-peg.” JPEGs have the file extension, “jpg”
Jumplists: Lists of recently modified documents in certain programs in Windows from Windows 7 onward. May be used to help determine a history of use of certain files that may be expanded beyond the standard file date attributes.
Keylogger: A program or device designed to keep a record of the keys types on a computer. May be used for monitoring, or espionage, such as to collect passwords. Some keyloggers may be accessed remotely.
Keyword search: A common technique used in computer forensic and electronic discovery, a keyword search is usually performed to find and identify every instance on a computer or other media of a given word or phrase, even if said word or phrase occurs in unallocated space or in deleted files.
Kilobyte (KB): 1024 bytes. Used to measure both storage and memory. Often considered (incorrectly) to be one thousand bytes.
LNK files: Windows creates LNK files when a user opens a local or remote file, and references both the original file along with date and time attributes about a file that has been opened.
Log files, or logfile: A record kept by many applications and operating systems of various activities by saving to a file – the logfile.
Mail Server: A server on a network that processes incoming and outgoing electronic communications, especially email. A mail server generally has security policies in place to allow only authenticated users access to given email communication. The mail server may store a copy of users’ data in various forms, or may not store copies of users’ data. A mail server may be utilized for multiple functions, including as a File Server, Application Server, or Backup Server.
Megabyte (MB): 1024 Kilobytes (KB), or 1,048,576 bytes. Often considered (incorrectly) to be one million bytes.
MAC dates: File attributes in the Windows operating system. Thee MAC dates are the date a file was last Modifies, Last Accessed, and Created.
Master File Table, or MFT: In an NTFS file structure (used in most versions of Windows from 1993-2014 (so far). The MFT contains substantial metadata about all files in a given volume, including file physical locations, MAC dates (times), file permissions, file size, the file’s parent directory, entry modification time, and at times, the entire content of small files.
Megabyte (MB): 1024 Kilobytes (KB), or 1,048,576 bytes. Often considered (incorrectly) to be one million bytes.
Memory Cache: Also known as RAM cache, it is high-speed memory designed to store frequently accessed or recently accessed data for quick use. On the Macintosh, RAM cache may also be disk cache.
Native format, native environment: The original configuration or program in which a file or other data was produced.
Network: A group of computers electronically linked so as to be able to share files or other resources, or for electronic communication. The World Wide Web is a particularly large network.
NTFS: NEW Technology FIle System. An operating system developed by Microsoft and released in 1993 with Windows NT 3.1. It has subsequently been used in versions of Windows through Windows 8.1. Previous versions of Windows had been dependent on the DOS operating system.
Operating System, OS: The suite of programs that allow a computer to operate. The OS controls signals from and to input devices (such as mouse, keyboard, microphone), peripherals (such as hard disks, CD-ROM drives, and printers), output devices (such as monitors and speakers) and performs the basic functions needed for a computer to operate. Common operating systems include Windows XP, Macintosh OS X, and Linux.
Page File: See Windows Swap File
Partition: A logical delineation on a disk drive such that a single drive acts as two, smaller disk drives.
PDA: Personal Digital Assistant. A handheld device that may have multiple functions, one of which is usually a form of electronic data. PDAs may contain programs, data files and storage, a digital camera and associated storage, a telephone and associated address / phone book and other data.
PDF: An Adobe Acrobat document. A common format for graphic and text files that is not easily altered. Stands for Portable Document Format.
Petabyte: 1024 Terabytes, or 1,125,899,906,900,000 bytes – a bit more than a quadrillion bytes
Program: Also known as an Application, or (sometimes) Software. The software used to access and create files or documents. Microsoft Word and Corel WordPerfect are applications that work with word processing documents. Microsoft Excel and Lotus 1-2-3 are applications that work with or spreadsheets.
Protocol: An agreed-upon standard format for communicating, connecting, or transferring data between two computers or devices. There are many communications protocols, such as TCP (Transmission Control Protocol).
RAM: Random Access Memory. Computer chips that store digital data in electronic form.
Registry Hives: The Windows registry is made up of sub files called “hives.” Individual Windows User settings and some history of usage are kept in the various hives and may be updated as the computer is used.
- SAM Hive: “Security Account Manager” that stores Users’ passwords
- Software Hive: Contains software and Windows settings
- System Hive: Contains information about the Windows system setup, mounted devices, alternative configurations for hardware drivers and services.
Sector: The basic and smallest unit of data storage on a hard disk or other electronic media. Generally consists of one contiguous area able to hold 512 bytes of data.
Server: A computer on a network that shares data with other computers on the network.
Shadow Volume: Also known as Shadow Copy, Volume Snapshot Service, Volume Shadow Copy Service, or VSS, is included with Microsoft Windows and makes automated backup copies of some files and operating system components from time to time on NTFS-based computers.
Software: Anything that can be stored electronically. Includes programs, files, and data.
Spoliation: Intentional, negligent, or accidental destruction or alteration of evidence.
Standalone: A computer that is not connected to a network.
Steganography: A means of writing hidden messages such that only the intended recipient knows of its existence. An modern example may be the replacing a few pixels of a digital image with a digital message. The slight change in the image may be unnoticeable to a person who does not know where in the image to look. Older forms of Steganography, which means “covered writing” in Greek, date back more than 2.000 years.
TCP/IP: A suite of communications protocols used to allow communication between computers on a network, such as on the Internet. Stands fro Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol.
Terabyte: 1024 Gigabytes, or 1,099,511,627,800 bytes – a bit more than one trillion bytes.
Thumbnail: Generally stands for a small, low-resolution image that takes the place of an original full-resolution image. Thumbnails do not generally contain metadata with GPS location or date of original creation of the source image.
TOR: Stands for “The Onion Router. TOR is US Government-created (through the US Naval Research Lab) software designed to allow anonymous or semi-anonymous communication.
Unallocated: The area on a hard disk or other media that is not (or is no longer) assigned to a file by the Operating System. May contain intact deleted files, remnants thereof, or other data.
User: A common term for the person using a computer, also referred to as an End User.
Web Browser: Often simply referred to as “browser.” A program used to find and display web pages. Popular browsers as of this writing are Microsoft Internet Explorer) often abbreviated as “Explorer,” Netscape Navigator, Mozilla Firefox, and Apple Safari.
Windows Registry: Microsoft Windows (“Windows”) keeps a large amount of information regarding the User’s Windows use and configuration in a part of the operating system called the Windows Registry. Included in the information kept in the Windows Registry is information such as that kept in Jump Lists and LNK files, and other data found in the Registry Hives.
Windows Swap File: Also known as the Page file, or Pagesys file. A virtual memory file used by Microsoft Windows as a kind of scratch pad during most operations. The Swap file is usually quite large and often contains records of operations or remnants of files not found elsewhere.
World Wide Web: A system of servers connected through the Internet that support HTML documents.
Yottabyte: 1024 zettabytes.
Zettabyte: 1024 exabytes.
